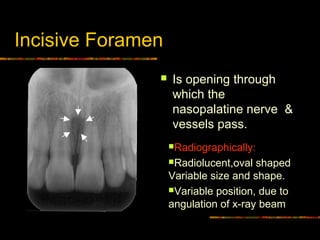
incisive canal radiograph
The mean width of bone anterior to the incisive canal was 632 143 mm. The incisive canal also known as the nasopalatine canal is an interosseous conduit through the anterior maxilla connecting the oral and nasal cavities.

Periapical Radiographs Obtained At First Visit A Radiopaque Structure Download Scientific Diagram
Root resorption and tooth displacement may be present.

. It is opens between the roots of the maxillary central incisors on the lingual. Usually only the inferior border of the orbit is visible over the panoramic radiograph Incisive canal. Table 3 shows the values obtained utilizing the GEE model to evaluate the influence of gender side examiner and type of examination on the probability of identifying MIC.
It is seen on both intraoral radiographs and extraoral radiographs. This canal may also be referred to as the incisive canal. In addition the angulation of the X-ray beam in panoramic radiography is about 78 from below.
However complications may arise due to an extension anterior to the mental foramen that forms the mandible incisive canal MIC. The region between mental foramens is considered as a zone of choice for implants. This might be explained by the fact that the incisive canal is less corticalized and has a smaller diameter than the mandibular canal.
Results The incisive canal was found in 87 of the scans. The incisive foramen generally appears in most panoramic radiographs though not with the clarity seen in periapical radiographs. Assessment of the mandibular incisive canal by panoramic radiograph and cone-beam computed tomography Objectives.
They may appear heart-shaped if the anterior nasal spine is superimposed. Panoramic radiographs can be used for visualization of the mental foramen and a potential anterior looping but not for locating the mandibular incisive canal. The anatomy of this area and especially the knowledge for the existence of the MIC is very important for the dentist and the oral surgeon because common surgical procedures performed in this area such as insertion of.
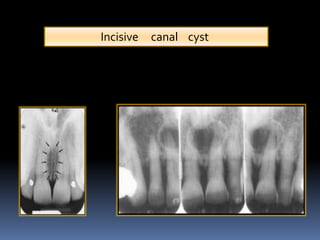
The most frequent symptom is swelling and difficulty in nasal breathing. The pear-shaped radiolucency between the apices of the central incisors can be mistaken for periapical pathology or cyst formation. White the median palatine cyst is an extension of the incisive canal cyst.
Rarely patients complain. FIGURE 2-5 Radiographs of maxillary incisor teeth often have periapical chevron-shaped lucencies that appear radiographically similar to lesions of endodontic origin LEO The trabecular bone and vascular channels around the apices contrasted with the dense compact bone of the alveolar walls and incisive bone create this effect. It is classified as a soft tissue cyst.
Within this canal lies the nasopalatine nerve and the vascular anastomosis between the greater palatine and sphenopalatine arteries. The nasopalatine canal presents as a vertical radiolucent band between the roots of the maxillary central incisors superiorly to the Post topics. The mandibular incisive canal mental foramen and associated neurovascular bundles exist in different locations and possess many variations.
Its appearance is quite variable due to normal anatomic variation and due to the operators angulation of the x-ray beam. Coronoid process is the thin triangular-shaped process of the anterosuperior aspect of the ramus. Individual gender age race assessing technique used and degree of edentulous alveolar bone atrophy largely influence these variations.
However complications may arise due to an extension anterior to the mental foramen that forms the mandible incisive canal MIC. It is located in the maxilla in the incisive fossa midline in the palate posterior to the central incisors at the junction of the medial palatine and incisive sutures. The mean endpoint was approximately 1098 and 1026 mm anterior to the mental foramen for left and right side respectively without a.
The incisive foramen also known as nasopalatine foramen or anterior palatine foramen is the oral opening of the nasopalatine canal. On periapical x-ray images the incisive foramen is located in the midline between the roots of the central incisors. Our goal is to evaluate identification of MIC by both panoramic radiograph PAN and cone-beam computed tomography CBCT.
Contribs created this work entirely by myself color006400Contribs. Approximately 30 of cases contain respiratory epithelium 3. Its radiographic detection remained lower than for the mandibular canal or mental foramen but higher than for the visibility of the lingual foramen.
The incisive foramen is the inferior opening of the nasopalatine canal incisive canal. The purpose of the present study is to assess incisive canal characteristics using CBCT sections. Incisive Canal Cyst A developmental nonodontogenic cyst that arises from epithelial remnants of the nasopalatine incisive canal Adult onset Well delineated inverted pear shaped radiolucency interposed between the apices of teeth numbers 8 and 9 Root divergence common Teeth are vital Microscopic.
To verify its existence for. A well-defined incisive canal could be detected in the majority of spiral CT scans. It will appear as a round to ovoid radiolucent area between the roots.
Our goal is to evaluate identification of MIC by both panoramic radiograph PAN and cone-beam computed tomography CBCT. It can be single or multiple. Popularly known as nasopalatine canal is a radiolucent tube shaped area located in between the maxillary central incisors.
150 cases with bilateral MIC were analyzed. Radiographic features They are seen as a solitary well-defined oval or round unilocular radiolucency between central incisors 6 mm in diameter. The mandibular incisive canal MIC is described as an anterior extension of the mandibular canal anterior to the mental foramen containing a neurovascular bundle.
It suggests that the clinicians should carefully identify these. Periapical radiograph depicting the junction of the mandibular canal and the mandibular incisive canal near the mental foramen. 30 November 2010 1346 UTC Source Original text.
IiNasolabial Naso-extra alveolar Cyst The nasolabial cyst occurs outside the bone in the nasolabial folds below the ala nasi. The incisive canal located at the midline posterior to the central incisor is an important anatomic structure of this area to be considered while planning for immediate implant placement in maxillary central incisor region. However complications may arise due to an extension anterior to the mental foramen that forms the mandible incisive canal MIC.
Only in a very few radiographs will the incisive canal or nasopalatine canal be. Mean canal length was 1863 235 mm and males have significantly longer incisive canal than females. Mandible incisive canal MIC as identified by examiners in images of panoramic radiograph PAN and cone-beam computed tomography CBCT.
As age of the subjects increased incisive foramen diameter and incisive canal. SSE and respiratory. This results in some distortion of the actual mandibular anatomy and may lead to misinterpretation.

The Largest Nasopalatine Duct Cyst A Case Report And Literature Review

Visibility Of Mandibular Anatomical Landmarks In Panoramic Radiography A Retrospective Study Semantic Scholar

Maxillary Anterior Landmarks Intraoral Radiographic Anatomy Continuing Education Course Dentalcare Com

Figure 2 Assessment Of The Mandibular Incisive Canal By Panoramic Radiograph And Cone Beam Computed Tomography

Periapical Radiograph 1 Year After Treatment Bone And Teeth Showing Download Scientific Diagram
Intra Oral Radiographic Anatomical Landmarks
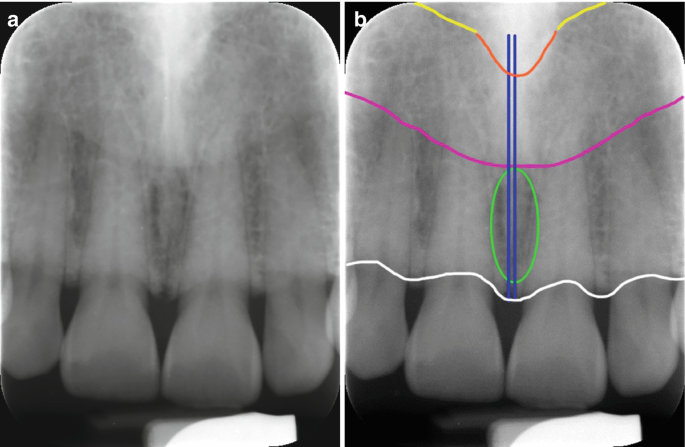
Normal Anatomical Landmarks In Dental X Rays And Cbct Springerlink

Identification Of Anatomical Landmarks On A Panoramic Radiograph 1 Download Scientific Diagram
File Nasolabial Duct Cyst Jpg Wikipedia
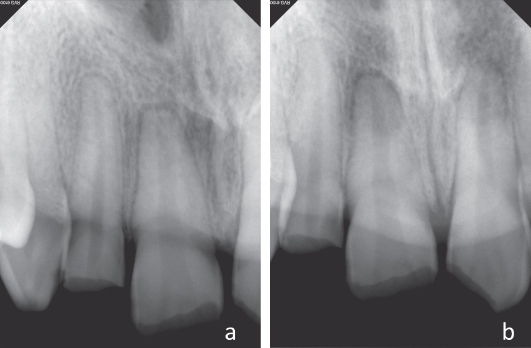
9 Radiographic Interpretation Of Traumatic Injuries Pocket Dentistry
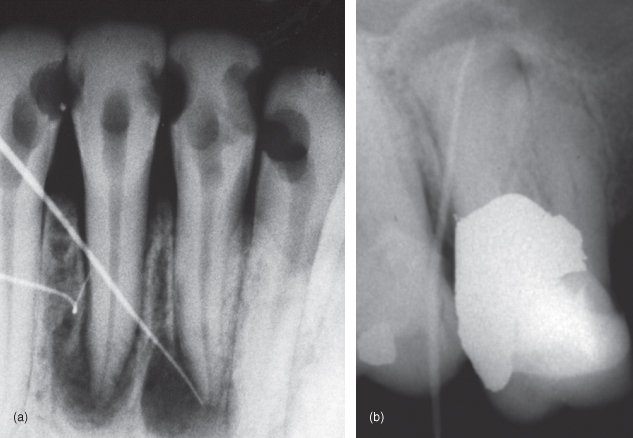
13 Radiographic Considerations During The Endodontic Treatment Pocket Dentistry

Interpretation Of Dental Radiographs In Dogs And Cats Part 2 Normal Variations And Abnormal Findings Today S Veterinary Practice

Superior Foramina Of The Nasopalatine Canal Dr G S Toothpix

Normal Anatomical Landmarks In Dental X Rays And Cbct Springerlink

Identification Of Anatomical Landmarks On A Panoramic Radiograph 1 Download Scientific Diagram

Normal Radiographic Anatomical Landmarks

Mouth Incisive Canal Cyst Professional Radiology Outcomes

Opg Showing Incisive Foramen And Mental Foramen Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment